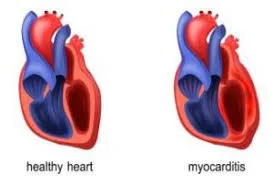
MYOCARDITIS
Inflammation of the myocardial wall.
ETIOLOGY :
·
Viruses
·
Bacteria
·
Fungi
·
Parasites
·
Radiation
·
Pharmacological
factors : drug such as lithium , cocaine
·
Chemical
factors
·
Toxic
agents such as lead
·
Connective
tissue disease .
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION :
§
Fever
§
Malaise
§
Fatigue
§
Dyspnea
§
Pharyngitis
§
Nausea
and vomiting
§
Chest
pain .
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION :
v
ECG
v
Laboratory
test (examination )
v
Myocardial
biopsy
v
Echocardiography
v
Gallium
scan
v
Chest
X-ray .
MANAGEMENT :
§
Digoxin
to treat ventricular failure
§
Oxygen
therapy
§
Provide
bed rest
§
Restricted
activity
§
Immune
suppressive therapy such as prednisone,cyclosprin.
§
Medication
such as –
Diuretics
Vein
and orbital dilator
Intrope
Angiotensin
inhibitor .
NURSING MANAGEMENT :
v
Decrease
cardiac output is an ongoing nursing diagnosis in the care of the patient with
myocarditis .
v
Assess
for the sign and symptoms of congestive heart failure
v
Decrease
cardiac work load
v
Prescribed
medications that increase the heart contractility.
v
Careful
monitoring and evaluation of patient taking these medications are necessary .
v
Nurse
should assess the level of anxiety and help the patient to reduce anxiety .
v
Care
include monitoring for the complications and providing .







0 Comments