LYMPH NODES
1.
INTRODUCTION:
Lymph nodes are oval or bean-shaped organs.
2.
SITUTATION :
Lymph nodes are present in groups,along the
length of lymph vessels.
3.
SHAPE:
Oval or bean shape, size varies some are small as a pin
head and the largest are about the size of an almond.
4.
STRUCTURE :
v
Lymph nodes have an outer capsule of fibrous
tissue that dips down into the node substance forming partitions, or
trabeculae.
v
The main substance of the node consists of
reticular and lymphatic tissue containing many lymphocytes and macrophages.
v
As many as four or five afferent lymph vessels may
enter a lymph node while only one efferent vessel carries lymph away from the node.
v
Each node has a concave surface called the
hilum, where an artery enters and a vein and the efferent lymph vessel leave.
v
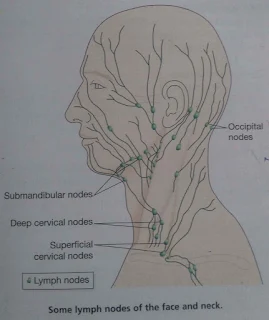
The large numbers of lymph nodes situated in
strategic positions throughout the body are arranged in deep and superficial
cervical needs.
v
Lymph from the head and neck passes through deep
and superficial cervical nodes.
v
Lymph from the upper limbs passes through nodes
situated in the elbow region,then through the deep and superficial axillary
nodes.
v
Lymph from organs and tissues in the thoracic cavity
drains through groups of nodes situated close to the mediastenium,large
airways,oesophagus and chest wall.
v
Most of the lymph from the breast passes through
the axillary nodes.
v
Lymph from the pelvic and abdominal cavities
passes through many lymph nodes before entering the cistern chyli.
5.
BLOOD SUPPLY:
The abdominal and pelvic nodes are situated
mainly in association with the blood vessels supplying the organs and close to
the main arteries, i.e. the aorta and
the external and internal iliac arteries.
6.
FUNCTIONS:
Ø
FILTERING AND PHAGOCYTOSIS .
§
Lymph is filtered by the reticular and lymphoid
tissue as it passes through lymph nodes.
§
Particulate matter may include microbes,dead and
alive phagocytes containing ingested microbes,cells from malignant
tumours,worn-out and damaged tissue cells and inhaled particles.
§
Organic material is destroyed in lymph nodes by
macrophages and antibodies.
§
In some cases where phagocytosis of microbes is
incomplete they may stimulate inflammation and enlargement of node.(lymphoadenopathy).
Ø
PROLIFERATION OF LYMPHOCYTES:
§
Activated T-and B-lymphocytes multiply in lymph
nodes.
§
Antibodies produced by sensitised B-lymphocytes enter lymph and blood draining
the node.












0 Comments