Diseases of
Intestine
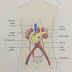
Structure of Intestine
Intestine
is divided into two parts, small intestine and large intestine.
Small intestine
1.It is
a 8 foot long tube. However due to relaxation of its muscle after death, its
length measure 20 to 21 feet at the time of a postmortem examination.
2.It
begins at the pyloric end of the stomach and ends at the caecum.
3.It is
divided into three parts.
.Duodenum
.Jejunum.
.Ileum.
4.It has
four layers.
.Serosa: Outer layer of visceral
peritoneum.
.Muscularis: Layer of smooth muscle
under the serosa.
.Submucosa: Layer of loose
connective tissue under the muscularis.
.Mucosa: Mucosa membrane lining
the lumen of the intestine.
5.Undigested
food is emptied into the large intestine.
6.The
following digestive juices are emptied into the small intestine for digestive
of food:-
Digestive Juices Emptied into Small Intestine
|
Source |
Digestive
juice |
|
Liver and gall
bladder |
Bile |
|
Pancreas |
Pancreatic juice. |
|
Small intestine |
Intestinal juice. |
Large Intestine
1.It is
a 5 feet long tube with a diameter of 2.5”.
2.It
extends from the end of ileum to the anus.
3.It has
the following parts:-
.Caecum.
.Colon.
.Rectum.
.Anal canal.
4.Caecum
is in continuity with the end of the ileum. Ileocecal valve is found at the
junction of the two. The appendix tissue in the appendix protects from infection.
5.The
wall of large intestine is thicker than that of the small intestine. There
longitudinal bands of smooth muscle along its outer surface called Taenia coli.
6.There
are small tags of fat attached to its outer surface called appendices epiploicae.
7.The Taenia
and appendices are not seen in the wall of the rectum and anal canal.
8.At the
lower end of the anal canal is the anal sphincters, external and internal.
Function
|
Part
of intestine |
Function |
|
Small intestine |
.Digestion of
food. .Absorption of
products of digestion of food. .Propulsion of
undigested food to the large intestine for excretion. |
|
Caecum |
.Receptacle at
the beginning of the large intestine. .Asorption of
water. |
|
Colon |
.Absorption of
water so that solid stool is formed. .Absorption of
electrolytes and glucose. .Propulsion of
undigested food to the rectum for excretion. |
|
Appendix |
.Presence of
large amount of lymphoid tissue protects from infection. It is a vestigial
organ.
|
|
Anal canal |
The anal
sphincters prevent passage of stool until it socially acceptable to pass
stool. |
Symptoms of Disturbance of Large
Intestine
Abnormal Stool
Abdominal
Colic.
Constipation.
Flatulence.
Diarrhoea.
Dysentery.
Observation of Stools
|
Variable |
Normal |
Abnormalities Feature |
Cause |
|
Colour |
Light or dark
brown |
Blackish |
.Green leafy
vegetables. .Iron therapy. .Upper intestinal
Haemorrhage. |
|
|
|
Clay |
.Jaundice. |
|
|
|
Red |
.Blood in stools. |
|
|
|
Pea soup |
.Typhoid. |
|
|
|
Rice Water |
.Cholera. |
|
Odour |
Sour |
Foul |
.Indigestion. |
|
|
Obnoxious. |
Rotten fish |
.Pus in stools |
|
|
|
Dysentery |
.Sour. |
|
Volume |
10 to 12 oz |
Large |
.Greater high
residue diet. |
|
Volume |
|
Low |
.Low residue
diet. .Fasting, with
only milk intake. |
|
Consistency |
Medium passed
easily. |
Hard |
.Constipation. |
|
|
|
Liquid |
.Diarrhoea. |
|
|
|
Blood and mucus |
.Dysentery. |
|
|
|
Rice water |
.Cholera. |
|
|
|
Pea soup |
.Typhoid. |
|
|
|
Froth ,oily |
.Hepatitis. |
|
Frequency |
1/ 2 per day. |
>2 days |
.Constipation. |
|
|
|
>2 days |
.Diarrhoea, dysentery,
colitis, cholera, indigestion. |
|
Reaction |
Slightly
alkaline. |
Acid |
.Diarrhoea, dysentery. |
|
Defecation |
Painless |
Painful and
difficult |
.Constipation .Fissure in anal. .Perianal
abscess. .Prolapsed,
thrombosed piles. |
|
|
|
With colic |
. Dysentery. .Gastroenteritis. |
|
Microscopy |
Undigested food particles |
Worms(round worm,
hook worm, thread worm),eggs of worms, E .histolytica, blood, mucus. |
|





0 Comments