” Polio Virus
General character : Polio virus belongs to the family picornoviridiae. It
has to majors groups, namely Entero
virus and Rhino virus. it affected all aged group people; more
particularly three typesof polio namely, spinal polio, Bulbar polio and Bulbo
spinal polio-
Spinal polio: In this type, the virus will affect
only the spine system but does not affect the brain or the spinal cord. This is
not a severe from the disease. However , it does not cause any symptoms in the
affected person.
Bulbar polio: Brainstem or CNS will be affected it does not cause
paralysis of the body.
Bulbospinal: It is a serious type of polio, in this spine as well
as the brainstem are affected. This poliomyelitis result in paralysis of the
body parts and results in serve disorders. This disease is even known as a
paralytic form of polio.
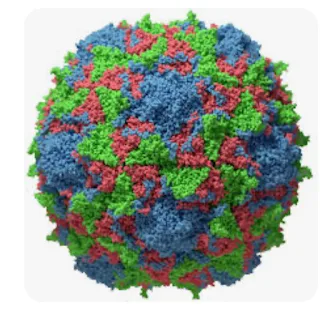
Morphology: It is small non enveloped spherical shaped virus. its size
measures approximately with 28nm to 38nm and to be appears with icosahedral
symmetry. It contains a specific proteins (VPI-VP4). As it possesses single
standard linear RNA, it belongs to the category of RNA virus.
Resistance : it is inactivated by heat at 550C for 30 minutes. However,
it is resistance to acidic PH.
Antigenic character: it has two antigens namely, C-antigens and
D-antigens. C-antigen is known as capsid antigen whereas D-antigen is dense
antigen.
C-antigen- it is less specific and associated
with the non-infection. Anti-c antibody does not neutralize virus infectivity.
D-antigen- it is more specific and associated with the virion.
Pathogenesis
Source – infected stool sample Oropharyngeal secretions
Reservoir -
Human being is only a reservoir
Mode of transmission
Feco-oral route
Ingestion – The virus may be transmitted through unhealthy-gienic practice with nails.
Inhalation – virus may be transmitted through airborne droplets.
Transmission rarely occurs through conjunctiva.
Contact- Close contact with patients leads to cause this infection.
Clinical symptoms: Incubation period is usually 1to 2 weeks. It is
characterized by in apparent infection, abortive infection, non-paralytic polio
and paralytic polio. Symptoms of Poliomyelitis
In apparent infection: Majority of the cases are
asymptomatic (91 to 96).
Abortive infection: It is characterized by the presence
of fever, malaise, sore-throat, anorexia, myalgia and headache (5% of case
develop above minor symptoms).
Non-paralytic polio: Usually it is seen in 1% of infected
case and develops with aseptic meanings.
Paralytic polio: It appears to be asymmetric acute
flaccid paralysis. Proximal muscle are affected paralysis beings at help at
hip.
Child can sit with flexed hip.
Over all symptoms :
Severe fever
Excess fatigue
Vomiting sensation
Pain in limbs
Sore throat
Frequent headaches back pain, leg pain
Stiffness in the muscles and neck areas
Limb deformities
Paralysis of some parts of the body
Sleeplessness
Develop weakness in the body
Problems with breathing
Drowsiness
Swelling in the throat
Lab diagnosis
Specimen : Throat
swab, rectal swab, CSF and blood
Culture cell line
Specimen is inoculated into primary monkey kidney cells, the
experimental setup subjected into incubation. After 3 to 4 days of incubation,
cytopathogenic effects must be observed. CPE develops with the features of
degeneration of entire cell sheet.
Antigen detection: It is performed by the mixing of isolated virus with
specific antiserum.
Antibody detection: Sera is collected from patient and mixed with specific
antigens.
Polio Vaccines: There are two of vaccines, Salk vaccine and Sabin vaccine.
Salk vaccine: It is otherwise called as IPV vaccine, it is killed
vaccine. It was prepared by Jonas Salk in 1950.
Preparation: Culturing of virus in monkey kidney cell line and treated with
formalin.
Schedule : Intra muscular route in 4 doses-first
three doses with 1 to 2 months gap. Fourth booster does has been given 6 to 12
months after third doses.
Advantage
1.
It is stable and safe
2.
Recommended
to people
3.
Does
not cause vaccine associated polio
Sabin Vaccine : This vaccine was developed by Albert Sabin in 1995. It is
otherwise called as live attenuated vaccine (OPV).
Preparation:
The virus will not
grow in presence of low level bicarbonate at 40oC and inactivated by specific
anti sera.
Schedule : Five doses are given totally- first, second,, third doses
given at 6/10/14.
Advantages :-
1.
Induces
herd immunity
2.
Provide
individual and community protection
3.
Induces
mucosal IgAproduction
4.
It
is very cheap
5.
Very
easy to administer.






0 Comments