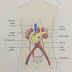
1. The endocrine system consists of glands widely separted from each other with no direct anatomical lines.
2. Endocrine glands consists of groups of secretory calls surrounded by a externsive network of capillaries which facilitates diffusion of hormons from the secretory cells into the blood stream.
3. They are commonly called as “ Ductless gland’s” because the hormones are secreted and diffuse directly into the blood stream.
4. They endocrine system consists of a number of distinct glands and some tissues in other organs.
THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS ARE
1. 1 PITUITARY GLAND
2. 2 THYROID GLAND
3. 4 PARATHYROID GLAND
4. 2 ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL GANDS)
5. THE PANCREATIC ISLETS (ISLETS OF LANGHERHANS)
6. 1 PINAL GLAND (OR) BODY
7. 1 THYMOUS GLAND
8. 2 OVARIS IN THE FEMALE
9. 2 TESTIS IN THE MALE.
Glands that discharge their secretion onto the epithelial surface of hollow organs,either directly or through a duct,are called EXOCRINE GLANDS.
<script async custom-element="amp-auto-ads"
src="https://cdn.ampproject.org/v0/amp-auto-ads-0.1.js">
</script>
Secretions of exocrine glands include mucus,saliva,digestive juices and earwax.
Exocrine glands vary considerably in size,shape and complexity.
Other glands discharge their secretions into blood and lymph,these are called ENDOCRINE GLANDS (Ductless gland) and their secretions are hormones.
Functions
1.keeps a surface moist.
2. provides lubricant for frictional surfaces.
3. enzymes for digestion
4. hormones for control and regulation of body functions
Thymus gland
Thymus gland
1. Introduction : it is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system.
2. Situation : the thymus gland lies in the upper part of the mediastinum behind the sternum and
extends upwards into the roof of the neck.
3. Weight :
10 -15gm during birth
30-40 gm during puberty
4. Organs associated with the thymus:
Anteriorly : sternum and upper four costal cartilages.
Posteriorly :aortic arch and its branches, brachiocephalic veins, trachea
Laterally: lungs
Superiorly : structures in the root of the neck
Inferiorly: heart
5. Structure:
The thymus gland consists of two lobes joined by areolar tissue.
The lobes are enclosed by a fibrous capsule which dips into their substance, dividing them into lobules that consist of an irregular branching framework of epithelial cells and lymphocytes.
6. Function:
munikrishnadn.blogspot.in
Lymphocytes originate from pluripotent stem cells in red bone marrow, those that enter the thymus develop into activated T-lymphocytes.
Thymic processing produces mature T-lymphocytes that can distinguish self tissue from foreign tissue, and also provides each T-lymphocyte with the ability to react to only one specific antigen from the millions it will encounter.
T-lymphocytes then leave the thymus and enter the blood.
Some enter lymphoid tissues and others circulate in the bloodstream.
T-lymphocytes production, although most prolific in youth, probably continues throught life from a resident population of thymic stem cells.
The maturation of the thymus and other lymphoid tissue is stimulated by THYMOSIN.
Thymosin is a harmone secreted by the epithelial cells that form the framework of the thymus gland.
Involution of the gland begins in adolescence and, with increasing age, the effectiveness of the T-lymphocyte response to antigens declines.
follow
THYROID GLAND
1. INTRODUCTION:- it is a highly vascular gland which is present in our endocrine system.
2. SITUATION:- It is situated in the neck in front of the larynx & Trachea.
3. SHAPE= “Butterfly Shape”
4. Stucture.
5. PARTS:
2 LOBES
1. Rt Lobe of thyroid gland
2. Lt lobe of thyroid gland
There are covering with the cartilage.
The lobes are probably cone shaped.
About 5 Cm long & 3 Cm wide.
6.BLOOD SUPPLY
Arterial supply: Inferior & Superior thyroid arteries.
Venous Drinage: internal Jugular vein.
7.Functions:
It stimulate the TSH.
8.Disorders of thyroid gland
1. Hyperthyroidism :- it increases secretion of TSH
2. Hypothyroidism :- it decreases Secretion of TSH
3. Goitre :- Enlargements of the Thyroid Gland.
4. Graands disease:
Function:
Production of thyroid gland
Secretion of the calcitonin Harmone.
PITUITARY GLAND
1. INTRODUCTION:- pituitary Gland and the hypothalamus act as a unit,
Regulating the activity of most of the other endocrine glands,
2. SITUATION : it lies in the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone below the hypothalamus.
3. MEASUREMENTS:
- Shape-pea,
- Weight- 500 mg.
4. BLOOD SUPPLY:-
ARTERIAL BLOOD:- This is supplied by branches from the internal carotid artery
VENOUS BLOOD:- Venous success b/w the layers of duramater.
FUNCTIONS OF PITUTARTARY GLAND
1. Production of growth harmone (GH)
a. It stimulates grow the & division of body cells
b. It regulates aspects of metabolism in many organs of liner (Intertwine & pamar)
2. If regulates & Stimulates growth hormone releasing harmone (GnRH)
3. Synthesis of Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH)
4. Releasing of ACTH (Adrenocticotropic hormone)
5. Stimulation of Prolactine harmone.
It helps for lactation
It acts directly on the breasts immediately after child birth.
6. It produces the gonadotrophin (Sex hormones')
GHRH= Growth hormone releasing hormone
GH= Growth Hormone.
GHRH= Growth hormone inhibiting harmone.
TRH= Thyroid releasing Harmone.
TSH= Thyroid Stimulating Hormone.
CRH= Corticotrophin releasing Hormone.
ACTH= Adrenocorticotrophic hormone.
PRH= prolactin releasing hormone.
PRL= prolactin.
LHRH= luteinizing hormone relearning hormone
GURH= gonadotropin releasing hormone.
RSH= Gonadotropin releasing hormone.
LH= Luteinising Hormone.
It consist of the
2 testis
2 epididymis
2 deferent ducts
2 seminal vesicles
2 ejaculatory ducts.
1 prostate gland
1 penis.
SCROTUM:-
Scrotum in a of deeply pigmented skin fibrous & connective tissue & smooth muscle
It is divided into 2 compartments each contains one, testis & 1 epididymis & the testicular end of a spermatic cord.
It lies below the symphysis pubis
1. INTRODUCTION: The testes are the reproduction gland of the male reproductive gland.
2. SITUATION:- it lies in the scrotum.
3. SHARE:- oval shape
4. MEASUREMENTS:
LENGTH - 4.5 cm
WIDE - 2.5 cm
THICKNESS - 3 cm
1. The Tunica vaginalis
2. Tunica albuginea.
3. Tunica Vasculosa
1. Tunica Vaginalis:- it is a outer covering of the Testis
It is double membrane forming structure.
2. Tunica albuginea:- this is a fibrous covering beneath the tunica vaginalis that surrounds the testis
It divides the glandular structure of the testis into lobules.
3. Tunica Vasculosa:- this consists of a network of capillaries supported by delicate connective tissue.
6. STRUCTURE OF THE TESTES:-
1. Testes are 200 to 300 lobules and within each lobule 1-4 convoluted loops composed of germinal epithelial cells, called seminiferous tubules.
Between the tubules there are groups of interstitial cells (of leydig)
It secrete testosterone hormone after puberty
Length of the tubule is 6 cm in full length & it is repeatedly folded & tightly packed into a mass called “the Epididymis)
Blood & lymph vessels pass to the Testis in the operatic cords.
FUNCTIONS:
Production of spermatozoa (Sperm)
Production of FSH
It helps for Spermatogenesis.
STRUCTURE OF THE SPERM.
PUBERTY IN THE MALE.
It occurs b/w the ages of 10 & 14.
L H from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland stimulate the interstial cells of the testis to increase the production of testosterone.
This Harmone influences the development of the body to sexual maturity.
THE CHANGES IN PUBERTY.
THE CHANGES IN PUBERTY.
Increases the growth of muscle, bone & Height & Weight.
enlargement of the larynx and Deeping of the voice it breaks.
enlargement of the larynx and Deeping of the voice it breaks.
Enlargement of the penis, scrotum & prostate gland.
Growth hair on the face axillae, chest, abdomen and pubis.
The skin thickens & Become more oilier.
1.INTRODUCTION: - ovaries are the female gonads (glands producing sex harmones and the ova)
2.SITUATION: - These lies on shallow fossa on the lateral wall of the pelvis.
3.MEASURMENTS:-
Length- 2.5 to 3.5 c.m long
Wide – 2 cm
Thick – 1 cm
b. Ligament: ovarian ligament – upper rest
Broad ligament –Lower
THE MEDULLA:-
This lies in the centre and consists of fibrous tissue blood vessels & nerves.
THE CORTEX:
Ø It surrounds the medulla.
Ø It has a Frame work of connective tissue, or stroma, covered by germinal epithelium.
Ø For 1 graffian follicle it later 28 days for matures, ruptures & releases its ovum into the peritoneal cavity. This is called ovulation & it occurs during most menstrual cycle.
ARTERIAL SUPPLY: ovarian arteries-which are branch from the abdominal aorta
VENOUSDRINAGE:
inferior venecava & left renal vein.
6.NERVE SUPPLY:-
The ovaries are supplied by para-sympathetic nerves from the sacral outflow
sympathetic nerves from the lumbar outflow.
sympathetic nerves from the lumbar outflow.
7.LYMPH DRAINAGE
This is to the lateral aortic and preaortic lymph nodes.
This is to the lateral aortic and preaortic lymph nodes.
FUNCTIONS:
1. Maturation Stimulation of FSH
2. Production of Luteinising Hormone.
3. Develop of Corpus luteum (Yellow body)
4. Corpus luteum produce the progesterone & Ocrthrocin.
5. Production of Human choroinic gonadotrophin (HCG)
It helps for 1st 3 months of the pregnancy.


































0 Comments