THALAMUS
v The
thalamus consist of large masses of grey matter.
v It
contains many nuclei.
v It
is predominantly a sensory relay station with incoming fibres from the spinal
cord and brain stem and onward fibres to the cerebral cortex.
v The
thalamus is the crude identification of stimuli such as pain.
v Variations
of temperature (or) touch is due to thalamic integration.
HYPOTHALAMUS:
v It
lies below the thalamus.
v Various
afferent and efferent connections of hypothalamus are responsible for its
functions.
v It
is having connections with limbic system.
v Nuclei
of tegmentum ,pons,hind brain and with pituitary gland.
FUNCTIONS:
v TEMPERATURE REGULATION:
normal body temperature is maintained by striking a balance
between heat production and heat loss.
1.
Temperature regulating centre in the
hypothalamus is sensitive to changes in temperature of blood and also receives
input from nerve fibres innervating temperature receptors in the skin.
2.
The hypothalamus regulates the secretion
of the anterior and posterior pituitary hormones.
3.
Regulation of body water and electrolyte
concentration .
4.
Maintenance of normal sexual desire,
behaviour and reproduction.
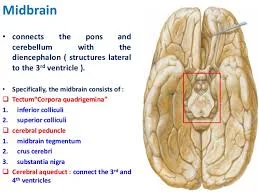
MIDBRAIN –(MESENCEPHALON):
1.
It is the shortest segment of the brain
stem, joins the forebrain above to the
pons and cerebellum below.
2.
Mid brain divided into right and left
cerebral peduncles .
3.
Two ventral portions of these are
distinctly separate from each other called CRURA CEREBRI.
A LAYER OF GREY MATTER
1.
A layer of grey matter –substantia nigra
seprates them from the dorsal part of the midbrain, which is continues across
the midline is known as TEGMENTUM.
2.
The matter is transversed by the cerebral
aqueduct which connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles.
3.
The part of the tegmentum dorsal to the
aqueduct is called tectum and it presents four rounded elevations known as the
COLLICULI.
4.
The upper pair super colliculi are visual
reflex centres and the lower pair super colliculi are visual reflex centres and
the lower pair inferior colliculi are auditory reflex centres.
5.
Mid brain is an important centre for
various righting and postural reflexes.
6.
These reflexes are being directed through
visual and auditory impulses.











0 Comments